Null-text Inversion for Editing Real Images using Diffusion Models
Paper Link: (https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09794)
Overview
Text guided Diffusion models are all the rage these days. A lot of people are trying to figure out how one can manipulate or edit the images using these state of the art tools.
In this blogpost we explore a technique called Null-Text Inversion for real image editing using text input. The authors of the paper achieve this in three steps:
-
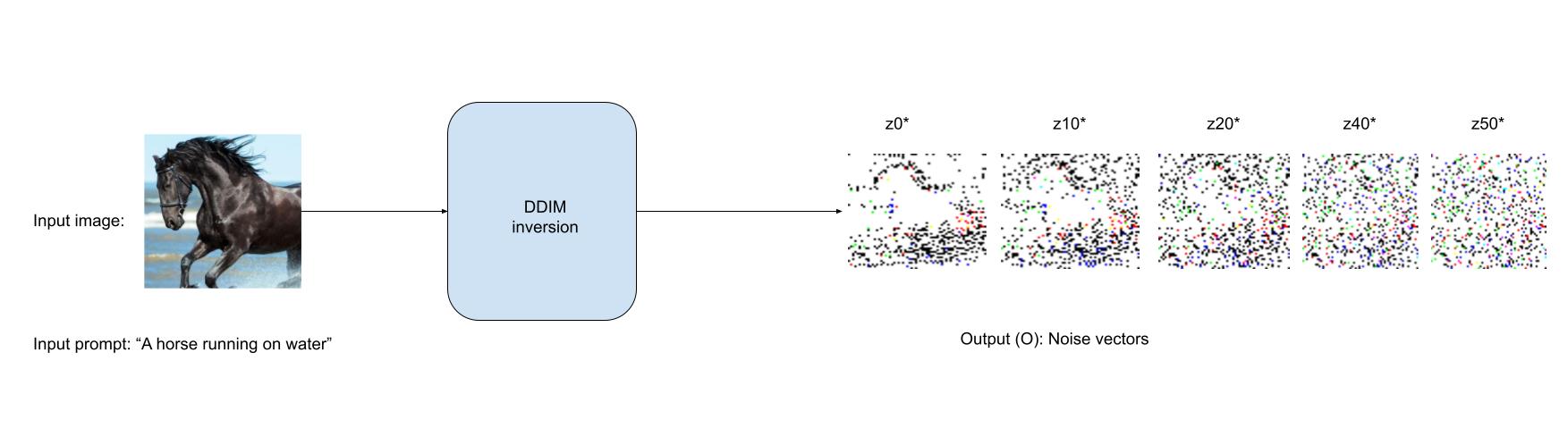
Inversion: The goal of this step is to find a noise vector that approximately produces the input image when fed with the input prompt into the diffusion process while preserving the editing capabilities of the model. Authors use DDIM inversion for this step.
-
Null-Text Optimisation: Optmizing the unconditional text embedding to invert the input image and the prompt.
-
Edited Image generation: Diffuse the image with edited prompt, optimized null-text embeddings and noise vector obtained from steps 2 and 1 respectively.
Code
Install packages
!pip install diffusers torch torchvision transformers matplotlib fastai
Imports
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline, DDIMScheduler
import torch
import requests
from PIL import Image
from io import BytesIO
import numpy as np
from fastai.vision.all import *
from fastai.vision.all import *
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
has_cuda = torch.cuda.is_available()
device = torch.device('cpu' if not has_cuda else 'cuda')
Setup Pipe
model_id_or_path = "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4"
scheduler = DDIMScheduler.from_config(model_id_or_path, subfolder="scheduler")
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
model_id_or_path,
safety_checker=None,
use_auth_token=True,
scheduler = scheduler,
).to(device)
Load inputs
image = Image.open("horse.png").convert("RGB")
image = image.resize((512, 512))
def preprocess_image(image):
image = np.array(image.convert("RGB"))
image = image[None].transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
image = torch.from_numpy(image).to(dtype=torch.float32) / 127.5 - 1.0
return image
pp_image = preprocess_image(image)
generator = torch.Generator(device=device)
latent = pipe.vae.encode(pp_image.to(device)).latent_dist.sample(generator=generator) * 0.18215
input_prompt = "a horse running on water"
text_embeddings = pipe._encode_prompt(input_prompt, device, 1, False, None)
DDIM Inversion
The goal of this step is to obtain a noise vector trajectory by gradually adding noise to the input image. Authors refer to this trajectory as a Pivot. Authors use a DDIM sampler to add noise in the input image over 50 timesteps.
@torch.no_grad()
def ddim_inversion(latents, encoder_hidden_states, noise_scheduler, unet):
next_latents = latents
all_latents = [latents.detach().cpu()]
# since we are adding noise to the image, we reverse the timesteps list to start at t=0
reverse_timestep_list = reversed(noise_scheduler.timesteps)
for i in range(len(reverse_timestep_list)-1):
timestep = reverse_timestep_list[i]
next_timestep = reverse_timestep_list[i+1]
latent_model_input = noise_scheduler.scale_model_input(next_latents, timestep)
noise_pred = unet(latent_model_input, timestep, encoder_hidden_states).sample
alpha_prod_t = noise_scheduler.alphas_cumprod[timestep]
alpha_prod_t_next = noise_scheduler.alphas_cumprod[next_timestep]
beta_prod_t = 1 - alpha_prod_t
beta_prod_t_next = 1 - alpha_prod_t_next
f = (next_latents - beta_prod_t ** 0.5 * noise_pred) / (alpha_prod_t ** 0.5)
next_latents = alpha_prod_t_next ** 0.5 * f + beta_prod_t_next ** 0.5 * noise_pred
all_latents.append(next_latents.detach().cpu())
return all_latents
num_inference_steps = 50
pipe.scheduler.set_timesteps(num_inference_steps, device=device)
all_latents = ddim_inversion(latent, text_embeddings, pipe.scheduler, pipe.unet)
Null-Text Optimisation
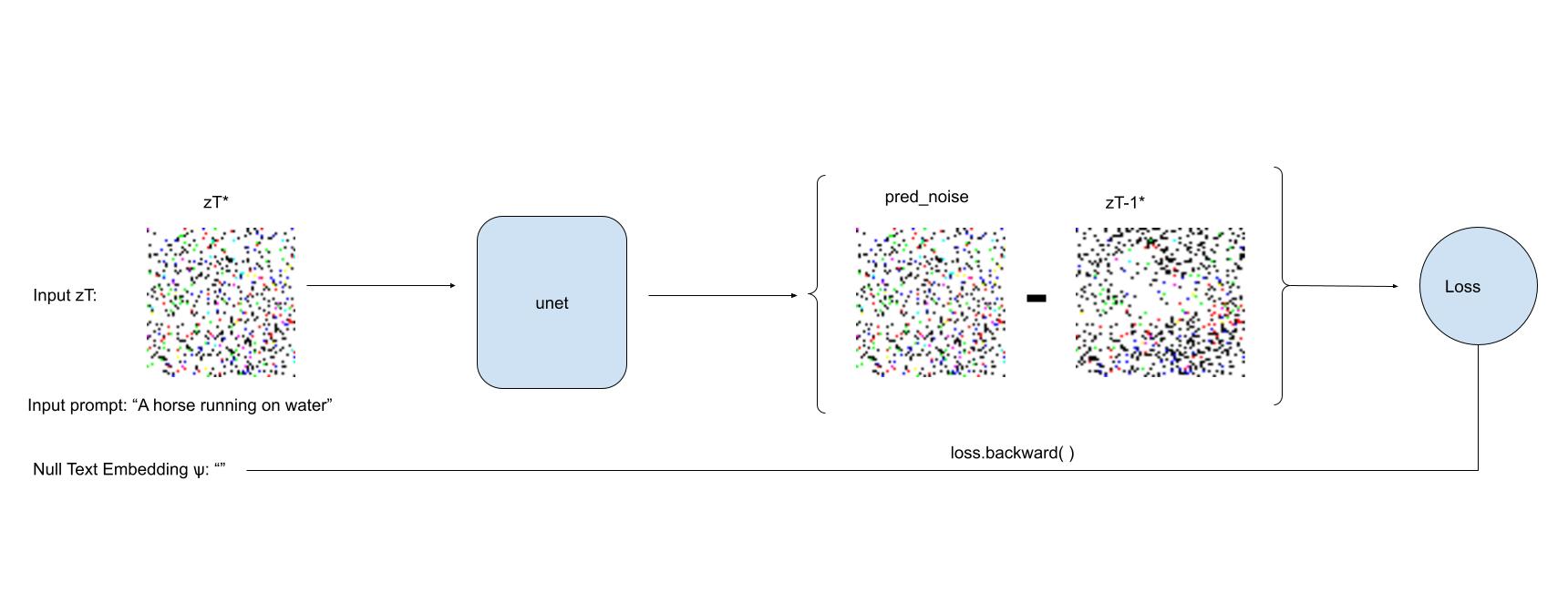
Unconditional or null-text embeddings significantly contribute to what the denoised image looks like. Our aim here is to find an optimised null-text embedding that can help us “invert” our input image.
To do that, we use the pivots obtained in step-1 as labels (since every pivot holds information about the input image). We now initialise a null-text embedding, and create a denoising trajectory starting with the last latent (z50*) obtained from Step-1.
We calculate the mse-loss between the noise prediction obtained by using ( zt* (t=50), input prompt and null-text embedding ) and the pivot zt*-1.
This loss is backpropagated and is used to update the null-text embeddings. The updated null-text embeddings will try to reduce the loss by predicting noise that is more similar to zt*-1, thereby including more artificats of the input image.
def null_text_inversion(
pipe,
all_latents,
prompt,
num_opt_steps=15,
lr=0.01,
tol=1e-5,
guidance_scale=7.5,
eta: float = 0.0,
generator = None
):
# initialise null text embeddings
null_text_prompt = ""
null_text_input = pipe.tokenizer(
null_text_prompt,
padding="max_length",
max_length=pipe.tokenizer.model_max_length,
truncaton=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
# prepare for optimising
null_text_embeddings = torch.nn.Parameter(pipe.text_encoder(null_text_input.input_ids.to(pipe.device))[0], requires_grad=True)
null_text_embeddings = null_text_embeddings.detach()
null_text_embeddings.requires_grad_(True)
# Initialize the optimizer
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(
[null_text_embeddings], # only optimize the embeddings
lr=lr,
)
# step_ratio = pipe.scheduler.config.num_train_timesteps // pipe.scheduler.num_inference_steps
text_embeddings = pipe._encode_prompt(prompt, device, 1, False, None).detach()
# input_embeddings = torch.cat([null_text_embeddings, text_embeddings], dim=0)
extra_step_kwargs = pipe.prepare_extra_step_kwargs(generator, eta)
all_null_texts = []
latents = all_latents[-1]
latents = latents.to(pipe.device)
for timestep, prev_latents in pipe.progress_bar(zip(pipe.scheduler.timesteps, reversed(all_latents[:-1]))):
prev_latents = prev_latents.to(pipe.device).detach()
# expand the latents if we are doing classifier free guidance
latent_model_input = pipe.scheduler.scale_model_input(latents, timestep).detach()
noise_pred_text = pipe.unet(latent_model_input, timestep, encoder_hidden_states=text_embeddings).sample.detach()
for _ in range(num_opt_steps):
# predict the noise residual
noise_pred_uncond = pipe.unet(latent_model_input, timestep, encoder_hidden_states=null_text_embeddings).sample
# perform guidance
noise_pred = noise_pred_uncond + guidance_scale * (noise_pred_text - noise_pred_uncond)
# compute the previous noisy sample x_t -> x_t-1
prev_latents_pred = pipe.scheduler.step(noise_pred, timestep, latents, **extra_step_kwargs).prev_sample
loss = torch.nn.functional.mse_loss(prev_latents_pred, prev_latents).mean()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
all_null_texts.append(null_text_embeddings.detach().cpu())
latents = prev_latents_pred.detach()
return all_latents[-1], all_null_texts
z_T, all_null_texts = null_text_inversion(pipe, all_latents, prompt, num_opt_steps=15)
Reconstruction
@torch.no_grad()
def reconstruct(pipe, latents, prompt, null_text_embeddings, guidance_scale=7.5, generator=None, eta=0.0):
text_embeddings = pipe._encode_prompt(prompt, device, 1, False, None)
extra_step_kwargs = pipe.prepare_extra_step_kwargs(generator, eta)
latents = latents.to(pipe.device)
for i, (t, null_text_t) in enumerate(pipe.progress_bar(zip(pipe.scheduler.timesteps, null_text_embeddings))):
# expand the latents if we are doing classifier free guidance
latent_model_input = torch.cat([latents] * 2)
latent_model_input = pipe.scheduler.scale_model_input(latent_model_input, t)
input_embedding = torch.cat([null_text_t.to(pipe.device), text_embeddings])
# predict the noise residual
noise_pred = pipe.unet(latent_model_input, t, encoder_hidden_states=input_embedding).sample
# perform guidance
noise_pred_uncond, noise_pred_text = noise_pred.chunk(2)
noise_pred = noise_pred_uncond + guidance_scale * (noise_pred_text - noise_pred_uncond)
# compute the previous noisy sample x_t -> x_t-1
latents = pipe.scheduler.step(noise_pred, t, latents, **extra_step_kwargs).prev_sample
#Post-processing
image = pipe.decode_latents(latents)
return image
Let’s visualise the inverted image
recon_img = reconstruct(pipe, z_T, prompt, all_null_texts, guidance_scale=1)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(20, 10))
ax[0].imshow(pp_image[0].permute(1,2,0).numpy() * 0.5 + 0.5)
ax[0].set_title("Original", fontdict={'fontsize': 40})
ax[0].axis('off')
ax[1].imshow(recon_img[0])
ax[1].set_title("Reconstructed", fontdict={'fontsize': 40})
ax[1].axis('off')
plt.show()
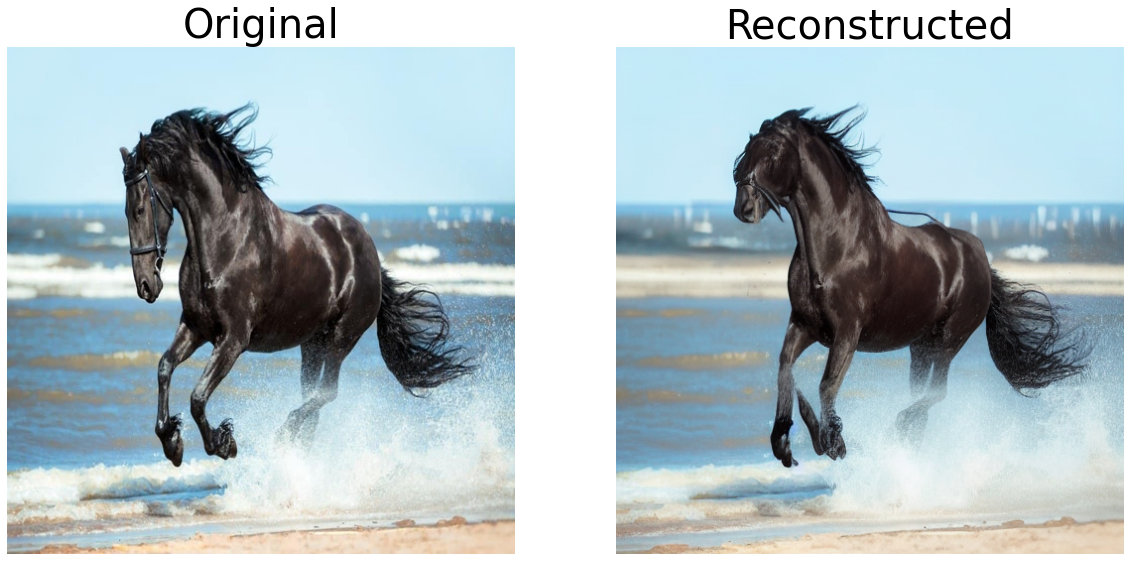

We have successfully inverted the input image i.e we have found the optimised null-text embedding and a latent, which when diffused with the input prompt, approximately reconstructs our input image. We can now perform the desired editing.
Editing the Inverted image
The final step is to take
- the noise vector obtained in step-1 (zT*)
- the optimised null-text emebdding obtained in step-2
- the edit prompt and diffusing them.
edit_prompt = "A zebra running on water"
edit_img = reconstruct(pipe, z_T, edit_prompt, all_null_texts, guidance_scale=1.0)
show_image(edit_img.squeeze())

edit_prompt = "A horse running in a city"
edit_img = reconstruct(pipe, z_T, edit_prompt, all_null_texts, guidance_scale=1.0)
show_image(edit_img.squeeze())

There is a lot of room for improvement but this is a good starting point. We can play with the guidance scale, loss function, etc. and see how it affects the image inversion. You can find the notebook here.
sources:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09794
https://github.com/tejank10/null-text-inversion